Tier 3 Rti for Reading and Math
How can Tier three intervention be implemented?
Page 5: Implementing Tier iii Reading Interventions
 One time students accept been identified as needing Tier iii intervention, it is time to start delivering more intensive, individualized teaching. High quality instruction in Tier 3 covers the core components of reading (i.e., phonemic awareness, phonics and word study, reading comprehension, vocabulary, fluency) and should be research validated. Many research-validated reading interventions are based on cardinal instructional principles:
One time students accept been identified as needing Tier iii intervention, it is time to start delivering more intensive, individualized teaching. High quality instruction in Tier 3 covers the core components of reading (i.e., phonemic awareness, phonics and word study, reading comprehension, vocabulary, fluency) and should be research validated. Many research-validated reading interventions are based on cardinal instructional principles:
-
Systematic teaching is that which is carefully planned and sequenced so that its lessons build on one another, moving from simple skills and concepts to more circuitous ones.
-
Explicit or direct educational activity involves education a specific skill or concept in a highly structured environment using clear, direct language. This type of instruction focuses on producing specific learning outcomes and is sometimes achieved through the use of scripted lessons. During explicit instruction, the teacher clearly identifies the expectations for learning, highlights important details of the concept or skill, provides precise instructions, and connects new learning to previous learned textile.
-
Immediate corrective feedback is provided as shortly equally possible following the performance of an activity to inform the student that his or her respond is inaccurate and to right his or her understanding of the skill or concept at event.
-
Frequent review is the practice of revisiting a skill or concept over fourth dimension to assess understanding and mastery and to ensure that the skill is maintained.
-
To aid students to maintain their previously mastered skills, teachers should provide students with opportunities to practice them. In addition, immediately after a skill has been taught, teachers should offer students opportunities to do it in order to build mastery. This tin include guided as well every bit independent do.
-
Scaffolded educational activity is a process during which a teacher adds instructional supports to raise a student'due south learning and aid in the mastery of a skill, concept, or task.

Activeness
After reviewing the definitions for the six primal instructional principles listed above, sentry the video clips below. For each video, select the instructional principle beingness highlighted.
Action A
explicit or straight instruction
scaffolded didactics
firsthand cosmetic feedback
opportunities to practice
(Close this panel)
Activity B
explicit or direct instruction
scaffolded educational activity
firsthand corrective feedback
opportunities to practice
(Close this panel)
Action C
explicit or direct educational activity
scaffolded pedagogy
immediate cosmetic feedback
opportunities to practice
(Close this panel)
"Copyright © past the Texas Teaching Agency and University of Texas at Austin. All rights reserved" on all Licensed Materials.
A schoolhouse or district can determine how finer a program covers the five core components and utilizes key instructional principles.
All-time Evidence Encyclopedia
http://www.bestevidence.org/
Center for Data-Driven Reform in Educational activity (John Hopkins University)
This online clearinghouse offers data on the researched evaluations of numerous educational programs in a coherently bundled and like shooting fish in a barrel-to-navigate format.
Big Ideas in Beginning Reading
http://reading.uoregon.edu/
Establish for the Development of Education Achievement, University of Oregon
This Website focusing on the five core components of reading offers information and resources to educators and parents with the goal of ensuring that all students are able to read at grade-level by the close of their third-course year.
The Florida Eye for Reading Inquiry
http://world wide web.fcrr.org/
Florida Country University Learning Systems Found
This site exists to broadcast research-validated information regarding literacy and assessment. Included are manufactures related to RTI implementation and information for principals nigh how to improve reading outcomes in their schools.
What Works Clearinghouse
https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/
U.S. Department of Education
Browse this site to read the latest from the U.S. Section of Education on topics related to "Kickoff Reading," "English Language Learners," and "Dropout Prevention." Online resources allow users to create their own "Effectiveness Rating" chart.
For Your Information
Whereas the v core components of reading take been demonstrated to be effective for native English speakers, more research is needed to decide their effectiveness for English language learners (ELLs) with learning disabilities.
 Rosa Parks Uncomplicated |
| Tier three: special pedagogy |
| Amount of daily didactics: 45 minutes; 5 days per week |
| Frequency of progress monitoring: ii times per week |
| Provider: special didactics teacher |
| Duration of educational activity: based on individual student'due south needs |
Every day, Laney receives 45 minutes of intensive, individualized educational activity in Tier 3 in addition to xc minutes of education in Tier 1. Ms. Jacobs, the special pedagogy instructor, provides the Tier 3 intervention. When Laney showtime begins Tier 3 intervention, Ms. Jacobs administers a brief reading cess and determines that Laney has difficulty with decoding. Using this information, Ms. Jacobs begins working with Laney on alphabetic character-sound correspondence and sight words. Afterwards three weeks of collecting progress monitoring data (six information points — two probes per week for 3 weeks) from Laney, Ms. Jacobs evaluates these data using a method known equally the four-betoken rule. She examines the relationship between the four most recent data points on Laney's graph and goal line. She uses these data to determine whether Laney is making acceptable progress toward the goals outlined in her individualized teaching plan (IEP).
x
individualized education program (IEP)
An individualized education program (IEP) is a working certificate that specifies individualized learning goals, in addition to any accommodations, modifications, and related services the child may need to attend school and to maximize learning.
- If Laney is not making progress and so Ms. Jacobs changes her instructional method.
- If Laney is responding to instruction, Ms. Jacobs continues with instruction.
- If Laney is surpassing her goal, Ms. Jacobs discusses her progress with the IEP team with an eye toward peradventure increasing Laney's goal.
Because Laney'due south last 4 information points are below the goal line, Ms. Jacobs changes her educational activity. In addition to having her work on alphabetic character-sound correspondence and sight words, Ms. Jacobs asks Laney to write the words she is reading and begins using decodable books, as opposed to merely give-and-take lists for reading exercise. 2 weeks later, Ms. Jacobs will again examine Laney'due south data (four data points) to determine whether to go along or to change her educational activity.
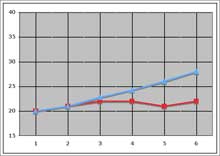
Laney graph: This graph shows Laney's information bespeak graph and goal line graph. The x-axis is labeled "1 through 6" in one-bespeak intervals. The y-axis is labeled "15 through twoscore" in v-point intervals. Laney'southward data points are in red and are as follows for weeks ane through 6: 20, 22, 23, 23, 21, and 23. Laney's goal line stretches from 20 at week 1 to 28 at week vi. Laney's first three data points are around the goal line, but her last three data points autumn beneath the goal line.
Heed as Doug and Lynn Fuchs discuss the characteristics that make special instruction unique and individualized.

Doug Fuchs, PhD
Nicholas Hobbs Endowed Chair
in Special Teaching and Human Evolution
Vanderbilt Academy, Nashville, TN
(fourth dimension: 0:24)
View Transcript

Lynn Fuchs, PhD
Nicholas Hobbs Endowed Chair
in Special Educational activity and Human Development
Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
(time: 0:19)
View Transcript
Transcript: Doug Fuchs, PhD
What should exist "special" nearly special didactics is that it should be data-based, individualized, and recursive, significant that the special education teacher uses an experimental approach to determine what effective pedagogy is for each kid. Information technology is not going to be known upward front what the right curriculum is for this kid, what the right instructional arroyo is for this kid.
Transcript: Lynn Fuchs, PhD
You have progress monitoring information, and you lot test the effectiveness of instructional components for a child. And you incorporate the ones that await constructive for that kid, and you drop other components that don't look effective. Then it'due south experimental for that kid.
Tier 3 Rti for Reading and Math
Source: https://iris.peabody.vanderbilt.edu/module/rti05/cresource/q2/p05/
0 Response to "Tier 3 Rti for Reading and Math"
Post a Comment